外部依赖太多,如何做单元测试?
事出有因
在日常的开发中,很多人习惯性地写完需求代码后,嗖的一声用 Postman 模拟真实请求或写几个 JUnit 的单元测试跑功能点,只要没有问题就上线了,但其实这存在很大风险,一方面无法验证业务逻辑的不同分支,另外一方面需严重依赖中间件资源才能运行测试用例,占用大量资源。
秣马厉兵
Mockito是一个非常优秀的模拟框架,可以使用它简洁的API来编写漂亮的测试代码,它的测试代码可读性高同时会产生清晰的错误日志。
添加 maven 依赖
1<dependency>
2 <groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
3 <artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
4 <version>3.3.3</version>
5 <scope>test</scope>
6</dependency>
注意:Mockito 3.X 版本使用了 JDK8 API,但功能与 2.X 版本并没有太大的变化。
指定 MockitoJUnitRunner
1@RunWith(MockitoJUnitRunner.class)
2public class MockitoDemoTest {
3
4 //注入依赖的资源对象
5 @Mock
6 private MockitoTestService mockitoTestService;
7 @Before
8 public void before(){
9 MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);
10 }
11}
从代码中观察到,使用 @Mock 注解标识哪些对象需要被 Mock,同时在执行测试用例前初始化 MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this) 告诉框架使 Mock 相关注解生效。
验证对象行为 Verify
1@Test
2public void testVerify(){
3 //创建mock
4 List mockedList = mock(List.class);
5 mockedList.add("1");
6 mockedList.clear();
7 //验证list调用过add的操作行为
8 verify(mockedList).add("1");
9 //验证list调用过clear的操作行为
10 verify(mockedList).clear();
11 //使用内建anyInt()参数匹配器,并存根
12 when(mockedList.get(anyInt())).thenReturn("element");
13 System.out.println(mockedList.get(2)); //此处输出为element
14 verify(mockedList).get(anyInt());
15}
存根 stubbing
stubbing 完全是模拟一个外部依赖、用来提供测试时所需要的数据。
1@Test
2public void testStub(){
3 //可以mock具体的类,而不仅仅是接口
4 LinkedList mockedList = mock(LinkedList.class);
5 //存根(stubbing)
6 when(mockedList.get(0)).thenReturn("first");
7 when(mockedList.get(1)).thenThrow(new RuntimeException());
8 //下面会打印 "first"
9 System.out.println(mockedList.get(0));
10 //下面会抛出运行时异常
11 System.out.println(mockedList.get(1));
12 //下面会打印"null" 因为get(999)没有存根(stub)
13 System.out.println(mockedList.get(999));
14 doThrow(new RuntimeException()).when(mockedList).clear();
15 //下面会抛出 RuntimeException:
16 mockedList.clear();
17}
- 存根(stub)可以覆盖,测试方法可以覆盖全局设置的通用存根。
- 一旦做了存根,无论这个方法被调用多少次,方法将总是返回存根的值。
存根的连续调用
1@Test
2public void testStub() {
3 when(mock.someMethod("some arg"))
4 .thenThrow(new RuntimeException())
5 .thenReturn("foo");
6 mock.someMethod("some arg"); //第一次调用:抛出运行时异常
7 //第二次调用: 打印 "foo"
8 System.out.println(mock.someMethod("some arg"));
9 //任何连续调用: 还是打印 "foo" (最后的存根生效).
10 System.out.println(mock.someMethod("some arg"));
11 //可供选择的连续存根的更短版本:
12 when(mock.someMethod("some arg")).thenReturn("one", "two", "three");
13 when(mock.someMethod(anyString())).thenAnswer(new Answer() {
14 Object answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) {
15 Object[] args = invocation.getArguments();
16 Object mock = invocation.getMock();
17 return "called with arguments: " + args;
18 }
19 });
20 // "called with arguments: foo
21 System.out.println(mock.someMethod("foo"));
22}
在做方法存根时,可以指定不同时机需要提供的测试数据,例如第一次调用返回 xxx,第二次调用时抛出异常等。
参数匹配器
1@Test
2public void testArugument{
3 //使用内建anyInt()参数匹配器
4 when(mockedList.get(anyInt())).thenReturn("element");
5 System.out.println(mockedList.get(999)); //打印 "element"
6 //同样可以用参数匹配器做验证
7 verify(mockedList).get(anyInt());
8
9 //注意:如果使用参数匹配器,所有的参数都必须通过匹配器提供。
10 verify(mock)
11 .someMethod(anyInt(), anyString(), eq("third argument"));
12 //上面是正确的 - eq(0也是参数匹配器),而下面的是错误的
13 verify(mock)
14 .someMethod(anyInt(), anyString(), "third argument");
15}
验证调用次数
1@Test
2public void testVerify{
3 List<String> mockedList = new ArrayList();
4 mockedList.add("once");
5 mockedList.add("twice");
6 mockedList.add("twice");
7 mockedList.add("three times");
8 mockedList.add("three times");
9 mockedList.add("three times");
10 //下面两个验证是等同的 - 默认使用times(1)
11 verify(mockedList).add("once");
12 verify(mockedList, times(1)).add("once");
13 verify(mockedList, times(2)).add("twice");
14 verify(mockedList, times(3)).add("three times");
15 //使用using never()来验证. never()相当于 times(0)
16 verify(mockedList, never()).add("never happened");
17 //使用 atLeast()/atMost()来验证
18 verify(mockedList, atLeastOnce()).add("three times");
19 verify(mockedList, atLeast(2)).add("five times");
20 verify(mockedList, atMost(5)).add("three times");
21}
验证调用顺序
1@Test
2public void testOrder()
3{
4 // A. 单个Mock,方法必须以特定顺序调用
5 List singleMock = mock(List.class);
6
7 //使用单个Mock
8 singleMock.add("was added first");
9 singleMock.add("was added second");
10
11 //为singleMock创建 inOrder 检验器
12 InOrder inOrder = inOrder(singleMock);
13
14 //确保add方法第一次调用是用"was added first",然后是用"was added second"
15 inOrder.verify(singleMock).add("was added first");
16 inOrder.verify(singleMock).add("was added second");
17}
以上是 Mockito 框架常用的使用方式,但 Mockito 有一定的局限性, 它只能 Mock 类或者接口,对于静态、私有及final方法的 Mock 则无能为力了。
而 PowerMock 正是弥补这块的缺陷,它的实现原理如下:
- 当某个测试方法被注解
@PrepareForTest标注后,在运行测试用例时会创建一个新的 MockClassLoader 实例并加载该测试用例使用到的类(系统类除外)。 - PowerMock 会根据你的 mock 要求,去修改写在注解
@PrepareForTest 里的 class 文件内容(调用非系统的静态、Final方法),若是包含调用系统的方法则修改调用系统方法的类的 class 文件内容达到满足需求 。
但值得高兴的是在 Mockito2.7.2 及更高版本添加了对 final 类及方法支持 。
同样, Mockito3.4.0 及更高版本支持对静态方法的 Mock,虽然是处于孵化阶段,但对于我们做单元测试而言是已经足够了。
决胜之机
大多数项目使用了 Spring 或 Spring Boot 作为基础框架,研发只需要关心业务逻辑即可。
在代码例子中将使用 Junit5 的版本,因此要求 Spring boot版本必须是2.2.0版本或以上,采用 Mockito3.5.11 的版本作为 Mock 框架,减少项目对 PowerMock 的依赖,另外还有一个重要原因是因为目前PowerMock不支持 Junit5,无法在引入 PowerMock 后使用Junit5 的相关功能及API,本文项目代码地址:https://github.com/GoQeng/spring-mockito3-demo。
maven 配置
1<properties>
2 <java.version>1.8</java.version>
3 <mockito.version>3.5.11</mockito.version>
4 <byte-buddy.version>1.10.15</byte-buddy.version>
5 <redisson-spring.version>3.13.4</redisson-spring.version>
6 <mysql.version>5.1.48</mysql.version>
7 <jacoco.version>0.8.6</jacoco.version>
8 <junit-jupiter.version>5.6.2</junit-jupiter.version>
9 <junit-platform.version>1.1.1</junit-platform.version>
10 <mybatis-spring.version>2.1.3</mybatis-spring.version>
11 <maven-compiler.version>3.8.1</maven-compiler.version>
12 <maven-surefire.version>2.12.4</maven-surefire.version>
13 <h2.version>1.4.197</h2.version>
14</properties>
15
16<dependencies>
17 <!-- spring boot相关依赖 -->
18 <dependency>
19 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
20 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
21 </dependency>
22
23 <dependency>
24 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
25 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
26 <scope>test</scope>
27 <exclusions>
28 <exclusion>
29 <groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
30 <artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
31 </exclusion>
32 <exclusion>
33 <groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
34 <artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
35 </exclusion>
36 </exclusions>
37 </dependency>
38
39 <!-- Mockito -->
40 <dependency>
41 <groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
42 <artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
43 <version>${mockito.version}</version>
44 <scope>compile</scope>
45 <exclusions>
46 <exclusion>
47 <groupId>net.bytebuddy</groupId>
48 <artifactId>byte-buddy</artifactId>
49 </exclusion>
50 <exclusion>
51 <groupId>net.bytebuddy</groupId>
52 <artifactId>byte-buddy-agent</artifactId>
53 </exclusion>
54 </exclusions>
55 </dependency>
56 <!-- 由于mockito-core自带的byte-buddy版本低,无法使用mock静态方法 -->
57 <dependency>
58 <groupId>net.bytebuddy</groupId>
59 <artifactId>byte-buddy</artifactId>
60 <version>${byte-buddy.version}</version>
61 </dependency>
62
63 <dependency>
64 <groupId>net.bytebuddy</groupId>
65 <artifactId>byte-buddy-agent</artifactId>
66 <version>${byte-buddy.version}</version>
67 <scope>test</scope>
68 </dependency>
69
70 <dependency>
71 <groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
72 <artifactId>mockito-inline</artifactId>
73 <version>${mockito.version}</version>
74 <scope>test</scope>
75 </dependency>
76
77 <!-- mybatis -->
78 <dependency>
79 <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
80 <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
81 <version>${mybatis-spring.version}</version>
82 </dependency>
83
84 <!-- redisson -->
85 <dependency>
86 <groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
87 <artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
88 <version>${redisson-spring.version}</version>
89 <exclusions>
90 <exclusion>
91 <groupId>junit</groupId>
92 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
93 </exclusion>
94 </exclusions>
95 <scope>compile</scope>
96 </dependency>
97
98 <!-- mysql -->
99 <dependency>
100 <groupId>mysql</groupId>
101 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
102 <version>${mysql.version}</version>
103 </dependency>
104
105 <!-- 代码覆盖率报表-->
106 <dependency>
107 <groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
108 <artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
109 <version>${jacoco.version}</version>
110 </dependency>
111
112 <!-- junit5 -->
113 <dependency>
114 <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
115 <artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
116 <version>${junit-jupiter.version}</version>
117 <scope>test</scope>
118 </dependency>
119
120 <dependency>
121 <groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
122 <artifactId>junit-platform-runner</artifactId>
123 <version>${junit-platform.version}</version>
124 <exclusions>
125 <exclusion>
126 <groupId>junit</groupId>
127 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
128 </exclusion>
129 </exclusions>
130 </dependency>
131
132 <!-- H2数据库-->
133 <dependency>
134 <groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
135 <artifactId>h2</artifactId>
136 <version>${h2.version}</version>
137 <scope>test</scope>
138 <exclusions>
139 <exclusion>
140 <groupId>junit</groupId>
141 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
142 </exclusion>
143 </exclusions>
144 </dependency>
145</dependencies>
146
147<build>
148 <plugins>
149 <plugin>
150 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
151 <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
152 <version>${maven-surefire.version}</version>
153 <executions>
154 <!--指定在mvn的test阶段执行此插件 -->
155 <execution>
156 <id>test</id>
157 <goals>
158 <goal>test</goal>
159 </goals>
160 </execution>
161 </executions>
162 <configuration>
163 <forkMode>once</forkMode>
164 <skip>false</skip>
165 <includes>
166 <include>**/SuiteTest.java</include>
167 </includes>
168 </configuration>
169 </plugin>
170 <plugin>
171 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
172 <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
173 <version>${maven-compiler.version}</version>
174 <configuration>
175 <source>8</source>
176 <target>8</target>
177 </configuration>
178 </plugin>
179 <plugin>
180 <groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
181 <artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
182 <version>${jacoco.version}</version>
183 <executions>
184 <execution>
185 <goals>
186 <goal>prepare-agent</goal>
187 </goals>
188 </execution>
189 <!-- attached to Maven test phase -->
190 <execution>
191 <id>report</id>
192 <phase>test</phase>
193 <goals>
194 <goal>report</goal>
195 </goals>
196 </execution>
197 </executions>
198 </plugin>
199 </plugins>
200</build>
201<reporting>
202 <plugins>
203 <plugin>
204 <groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
205 <artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
206 <reportSets>
207 <reportSet>
208 <reports>
209 <!-- select non-aggregate reports -->
210 <report>report</report>
211 </reports>
212 </reportSet>
213 </reportSets>
214 </plugin>
215 </plugins>
216</reporting>
maven 运行测试用例是通过调用 maven 的 surefire 插件并 fork 一个子进程来执行用例的。
forkMode 属性指明是为每个测试创建一个进程还是所有测试共享同一个进程完成,forkMode 设置值有 never、once、always 、pertest 。
- pretest:每一个测试创建一个新进程,为每个测试创建新的JVM进程是单独测试的最彻底方式,但也是最慢的,不适合持续回归。
- once:在一个进程中进行所有测试。once 为默认设置,在持续回归时建议使用默认设置。
- always:在一个进程中并行的运行脚本,Junit4.7 以上版本才可以使用,surefire 的版本要在 2.6 以上提供这个功能,其中 threadCount 执行时,指定可分配的线程数量,只和参数 parallel 配合使用有效,默认为 5。
- never:从不创建新进程进行测试。
环境准备
在项目中 test 目录下建立测试入口类 TestApplication.java,将外部依赖 Redis 单独配置到 DependencyConfig.java 中,同时需要在 TestApplication.class 中排除对 Redis 或 Mongodb 的自动注入配置等。
注意:**将外部依赖配置到DependencyConfig并不是必要的,**此步骤的目的是为了避免每个单元测试类运行时都会重启 Spring 上下文,可采用 @MockBean 的方式在代码中引入外部依赖资源替代此方法。
1@Configuration
2public class DependencyConfig {
3
4 @Bean
5 public RedissonClient getRedisClient() {
6 return Mockito.mock(RedissonClient.class);
7 }
8
9 @Bean
10 public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
11 return Mockito.mock(RestTemplate.class);
12 }
13}
接着在测试入口类中通过 @ComponentScan 对主入口启动类 Application.class 及 RestClientConfig.class 进行排除。
1@SpringBootApplication
2@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = @ComponentScan.Filter(
3 type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,
4 classes = {Application.class, RestClientConfig.class}))
5@MapperScan("com.example.mockito.demo.mapper")
6public class TestApplication {
7
8}
为了不单独写重复的代码,我们一般会把单独的代码抽取出来作为一个公共基类,其中 @ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class) 注解目的是告诉 Spring boot 将使用 Junit5 作为运行平台,如果想买中使用 Junit4 的话,则需要使用 @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) 注解告知用 SpringRunner 运行启动。
1@SpringBootTest(classes = TestApplication.class)@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
2public abstract class SpringBaseTest {}
准备好配置环境后,我们便可以开始对项目的 Mapper、Service、Web 层进行测试了。
Mapper层测试
对 Mapper 层的测试主要是验证 SQL 语句及 Mybatis 传参等准确性。
1server:
2 port: 8080
3spring:
4 test:
5 context:
6 cache:
7 max-size: 42
8 main:
9 allow-bean-definition-overriding: true
10 datasource:
11 url: jdbc:h2:mem:test;MODE=MYSQL;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1;INIT=runscript from 'classpath:init.sql'
12 username: sa
13 password:
14 driverClassName: org.h2.Driver
15 hikari:
16 minimum-idle: 5
17 maximum-pool-size: 15
18 auto-commit: true
19 idle-timeout: 30000
20 pool-name: DatebookHikariCP
21 max-lifetime: 1800000
22 connection-timeout: 10000
23 connection-test-query: SELECT 1
24
25mybatis:
26 type-aliases-package: com.example.mockito.demo.domain
27 mapper-locations:
28 - classpath:mapper/*.xml
对 Mapper 层的测试并没有采取 Mock 的方式,而是采用 H2 内存数据库的方式模拟真实数据库,同时也避免由于测试数据给真实数据库带来的影响。
1jdbc:h2:mem:test;MODE=MYSQL;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1;INIT=runscript from 'classpath:init.sql'
配置 H2 数据库信息,同时 INIT 指定在创建连接时会执行类路径下的 init.sql 即建表 SQL 。
1public class DemoMapperTest extends SpringBaseTest {
2
3 @Resource
4 private DemoMapper demoMapper;
5
6 @Test
7 public void testInsert() {
8 Demo demo = new Demo();
9 demo.setName("test");
10 demoMapper.insert(demo);
11
12 Integer id = demo.getId();
13 Demo model = demoMapper.getDetail(id);
14 Assert.assertNotNull(model);
15 Assert.assertEquals(demo.getName(), model.getName());
16 }
17
18 @Test
19 public void testGetList() {
20 Demo demo = new Demo();
21 demo.setName("test");
22 demoMapper.insert(demo);
23
24 List<Demo> demoList = demoMapper.getList();
25 Assert.assertNotNull(demoList);
26 Assert.assertEquals(1, demoList.size());
27 }
28}
Service层测试
一般项目的业务逻辑写在 service 层,需要写更多的测试用例验证业务代码逻辑性及准确性,尽可能的覆盖到业务代码的分支逻辑。
1public class DemoServiceTest extends SpringBaseTest {
2
3 @Resource
4 private DemoService demoService;
5 @Resource
6 private RedissonClient redissonClient;
7
8 @Resource
9 private RestTemplate restTemplate;
10
11 @BeforeEach
12 public void setUp() {
13 MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
14 }
15
16 @Test
17 public void testGetList() {
18 //测试第一个分支逻辑
19 RAtomicLong rAtomicLong = Mockito.mock(RAtomicLong.class);
20 Mockito.when(redissonClient.getAtomicLong(ArgumentMatchers.anyString())).thenReturn(rAtomicLong);
21 long count = 4L;
22 Mockito.when(rAtomicLong.incrementAndGet()).thenReturn(count);
23 List<Demo> demoList = demoService.getList();
24 Assert.assertTrue(demoList != null && demoList.size() == 1);
25 Demo demo = demoList.get(0);
26 Assert.assertNotNull(demo);
27 Assert.assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(4), demo.getId());
28 Assert.assertEquals("testCount4", demo.getName());
29
30 //测试第二个分支逻辑
31 Mockito.when(redissonClient.getAtomicLong(ArgumentMatchers.anyString())).thenReturn(rAtomicLong);
32 count = 1L;
33 Mockito.when(rAtomicLong.incrementAndGet()).thenReturn(count);
34
35 MockedStatic<AESUtil> aesUtilMockedStatic = Mockito.mockStatic(AESUtil.class);
36 aesUtilMockedStatic.when(() -> AESUtil.encrypt(ArgumentMatchers.eq("test"), ArgumentMatchers.eq("1234567890123456")))
37 .thenReturn("demo");
38
39 demoList = demoService.getList();
40 Assert.assertTrue(demoList != null && demoList.size() == 1);
41 Demo encryptDemo = demoList.get(0);
42 Assert.assertNotNull(encryptDemo);
43 Assert.assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(1), encryptDemo.getId());
44 Assert.assertEquals("testEncrypt", encryptDemo.getName());
45
46 //测试第三个分支逻辑
47 Mockito.when(redissonClient.getAtomicLong(ArgumentMatchers.anyString())).thenReturn(rAtomicLong);
48 count = 1L;
49 Mockito.when(rAtomicLong.incrementAndGet()).thenReturn(count);
50
51 //执行真实方法
52 aesUtilMockedStatic.when(() -> AESUtil.encrypt(ArgumentMatchers.eq("test"), ArgumentMatchers.eq("1234567890123456")))
53 .thenCallRealMethod();
54
55 String mobileUrl = "https://tcc.taobao.com/cc/json/mobile_tel_segment.htm?tel=";
56 MobileInfoDTO mobileInfoDTO = new MobileInfoDTO();
57 mobileInfoDTO.setName("testMobile");
58 mobileInfoDTO.setLocation("testLocation");
59 Mockito.when(restTemplate.getForObject(mobileUrl, MobileInfoDTO.class)).thenReturn(mobileInfoDTO);
60 demoList = demoService.getList();
61 Assert.assertNotNull(demoList);
62 Assert.assertEquals(1, demoList.size());
63 Demo demo1 = demoList.get(0);
64 Assert.assertNotNull(demo1);
65 Assert.assertEquals(mobileInfoDTO.getName(), demo1.getName());
66 }
67}
WEB层测试
1public class DemoControllerTest extends SpringBaseTest {
2
3 private MockMvc mockMvc;
4
5 @Mock
6 private DemoService demoService;
7
8 //把demoService注入到demoController中
9 @InjectMocks
10 private DemoController demoController;
11
12 @BeforeEach
13 public void setUp() {
14 MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
15 //手动构建,不使用@AutoConfigureMockMvc注解避免重复启动spring上下文
16 this.mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(demoController).build();
17 }
18
19 @Test
20 public void addDemoTest() throws Exception {
21 String name = "mock demo add";
22 mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/demo")
23 .param("name", name))
24 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
25 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().string(containsString("OK")))
26 .andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print());
27 //验证调用次数,发生过一次
28 Mockito.verify(demoService, Mockito.times(1)).addDemo(ArgumentMatchers.any());
29 }
30
31 @Test
32 public void getDemoListTest() throws Exception {
33 mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/demos"))
34 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
35 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().string("[]"))
36 .andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print());
37 //验证调用次数,发生过一次
38 Mockito.verify(demoService, Mockito.times(1)).getList();
39 }
40
41 @Test
42 public void getDemoDetailTest() throws Exception {
43 String name = "mock demo getDetail";
44 mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/demo/{id}", 1))
45 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
46 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().string(containsString("")))
47 .andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print());
48 //验证调用次数,发生过一次
49 Mockito.verify(demoService, Mockito.times(1)).getDetail(ArgumentMatchers.anyInt());
50 }
51}
套件测试
当写完 mapper、service、web 层的单元测试后,我们便可以把这些单元测试类都打包到套件中,并在 maven surefire 插件指定需要执行的套件类,我们可以使用 @SelectPackages 或 @SelectClass 注解把要测试的类包含进来。
1@RunWith(JUnitPlatform.class)
2@SelectPackages("com.example.mockito.demo")
3public class SuiteTest {
4}
把测试套件配置到surefire插件中。
1<plugin>
2 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
3 <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
4 <version>${maven-surefire.version}</version>
5 <executions>
6 <!--指定在mvn的test阶段执行此插件 -->
7 <execution>
8 <id>test</id>
9 <goals>
10 <goal>test</goal>
11 </goals>
12 </execution>
13 </executions>
14 <configuration>
15 <forkMode>once</forkMode>
16 <skip>false</skip>
17 <includes>
18 <include>**/SuiteTest.java</include>
19 </includes>
20 </configuration>
21</plugin>
生成覆盖率报告
1<plugin>
2 <groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
3 <artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
4 <version>${jacoco.version}</version>
5 <executions>
6 <execution>
7 <goals>
8 <goal>prepare-agent</goal>
9 </goals>
10 </execution>
11 <!-- 绑定到test阶段 -->
12 <execution>
13 <id>report</id>
14 <phase>test</phase>
15 <goals>
16 <goal>report</goal>
17 </goals>
18 </execution>
19 </executions>
20</plugin>
项目中使用 jacoco 作为代码覆盖率工具,在命令行中运行 mvn clean test 后会执行所有单元测试用例,随后会在 target 目录下生成site 文件夹,文件夹包含 jacoco 插件生成的测试报告。
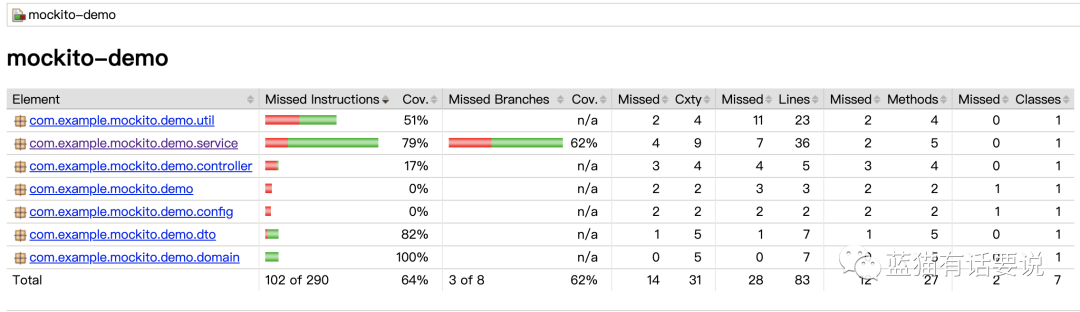
报告中主要包含本次测试中涉及到的类、方法、分支覆盖率,其中红色的表示未被覆盖到,绿色表示全覆盖,黄色的则表示部分覆盖到,可点击某个包或某个类查看具体哪些行未被覆盖等。

注意:
- test 测试目录与 main 开发目录的资源是相互隔离的。
- 使用
@MockBean会导致启动 Spring 上下文多次,影响测试效率。 - 使用
@AutoConfigureMockMvc注解导致 Spring 上下文多次重启,建议使用MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(demoController).build()构建。
言而总之
虽然编写单元测试会带来一定的工作量,但通过使用 Mockito 不仅可以保留测试用例,还可以快速验证改动后的代码逻辑,对复杂或依赖中间件多的项目而言,使用 Mockito 的优势会更加明显。
除此之外,更加重要的是我们自己可以创建条件来模拟各种情景下代码的逻辑准确性,保证代码的质量,提高代码维护性、提前发现潜在的问题,不再因为账号问题等导致测不到某些逻辑代码,使得项目上线也心里有底。